Cash in the Age of Digital Disruption: Insights from Southeast Asia
In the bustling streets of Southeast Asia, amidst the chaos of urban life and the tranquility of rural areas, a quiet revolution is underway – one that is changing the way people access and interact with their finances. Millions of people across the region depend on ATMs for their everyday needs, which has been integral to this transformation. However, with technology advancing and cashless transactions becoming more prevalent, the fate of ATMs hangs in the balance.
Countries such as Malaysia and the Philippines serve as representatives of trends shaping the ATM industry in the region. From the gleaming skyscrapers of Kuala Lumpur in Malaysia to the barangays (small territorial districts) in the provinces of the Philippines, the ATM plays a vital role in facilitating banking transactions and fostering financial inclusion. Yet, beneath the surface, transformational shifts are occurring, driven by advances in technology and changing consumer preferences.
Nevertheless, in this evolving era of finance, it is worth noting how Southeast Asia is still going strong with cash. Read on!
Adapting to the cashless era: The future of cash in Southeast Asia
Cash, long considered the lifeblood of economies worldwide, still holds a prominent place in the financial systems of Southeast Asian countries like Malaysia and the Philippines. While digital payment methods have gained traction, especially in urban centres, cash remains the preferred choice for many individuals and businesses, particularly in rural areas and informal sectors.
Therefore, rather than viewing digital payments as a replacement for cash, regulators have focused on creating an enabling environment where both payment methods can thrive, catering to the diverse preferences and needs of consumers.
However, consumer preferences are shifting in response to technological developments and changing lifestyles. Younger generations are increasingly adopting digital payment solutions for their convenience and efficiency, driving the integration of digital payment platforms into various sectors of the economy.
Despite it all, cash continues to maintain its relevance, accommodating diverse consumer preferences in shaping future payment system. In the Philippines, we can see via this chart below that there is still a demand for ATMs and that banks and third- party ATM providers are optimistic on the cash economy in the country.
Total number of ATMS in the Philippines from 2001 to 2029 – Forecasted (Thousands)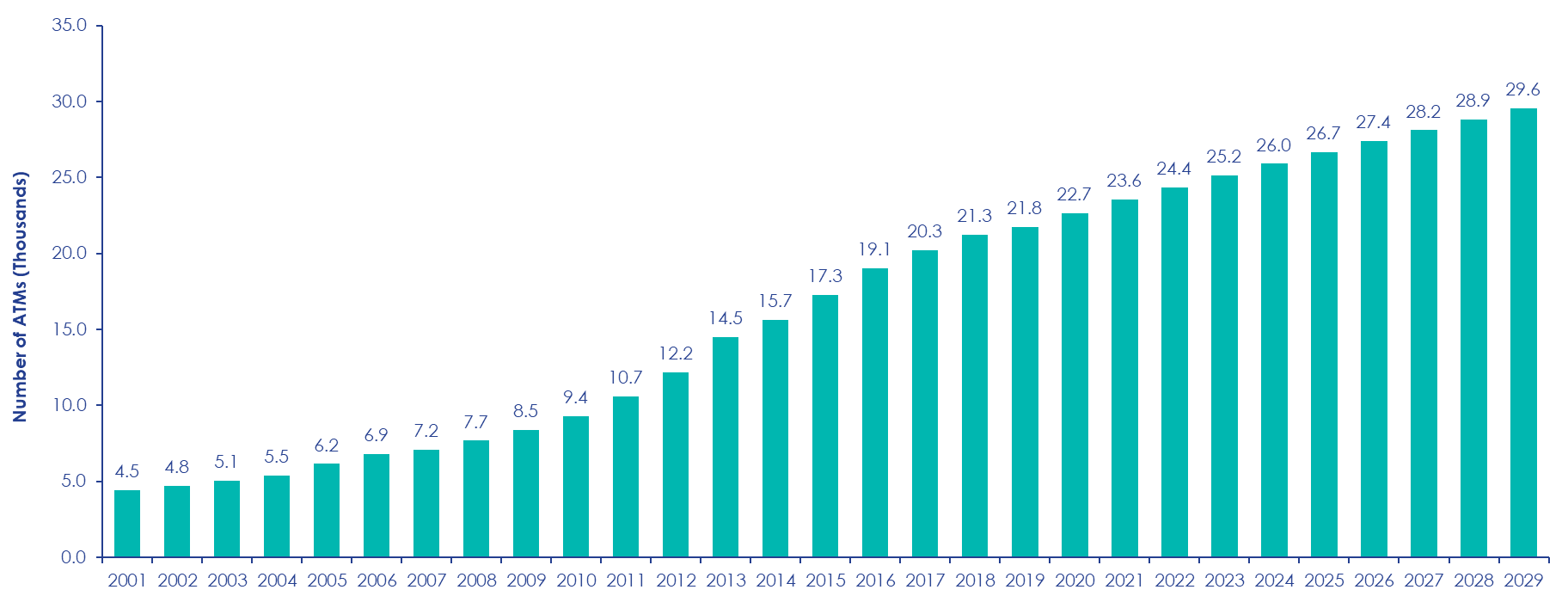
Source: Philippines: Total Number of ATMs in thousands 2001-2029 | Statista
Digging deeper into the impact of ATM network growth in Malaysia and the Philippines
Undeniably, the expansion of cashless payment options has reformed the financial scenario in Malaysia and the Philippines, yet the ATM network continues to play a crucial role in driving growth and accessibility within this evolving ecosystem.
As cashless transactions gain momentum, one might assume a decline in the relevance of physical cash and, by extension, traditional ATM services. However, the reality is quite the opposite. The ATM network acts as an important medium for consumers seeking to convert digital funds into physical cash. For e.g. in the Philippines, Euronet has tied up with GoTyme Bank, a digital bank to provide physical cash access to their customers through cobranded ATMs- making the bank phygital, rather than just remaining digital.
Despite the increasing popularity of digital wallets and mobile banking apps, there remains a persistent demand for cash, especially for small-value transactions, peer-to-peer payments, and in sectors where cash remains king. In April 2022, Malaysia gave five digital bank licences to successful applicants. While the premise is to increase banking penetration and improve financial inclusion, there will be a need for these digital banks to have a cash extension. That’s where 3rd party ATM providers can join hands with these digital banks to be their “cash arm” for the consumers.
The ATM network's expansion supports financial inclusion by reaching rural and underserved areas, ensuring equitable access to banking services. Despite the increasing popularity of cashless payments, the ATM network's growth highlights its resilience and adaptability within the banking infrastructure. ATMs continue to evolve with enhanced functionalities, improved security features, and increased accessibility, remaining a cornerstone of the financial ecosystem in Southeast Asia, driving growth, inclusivity, and interoperability.
Total number of ATMS in Malaysia from 2001 to 2029 – Forecasted (Thousands)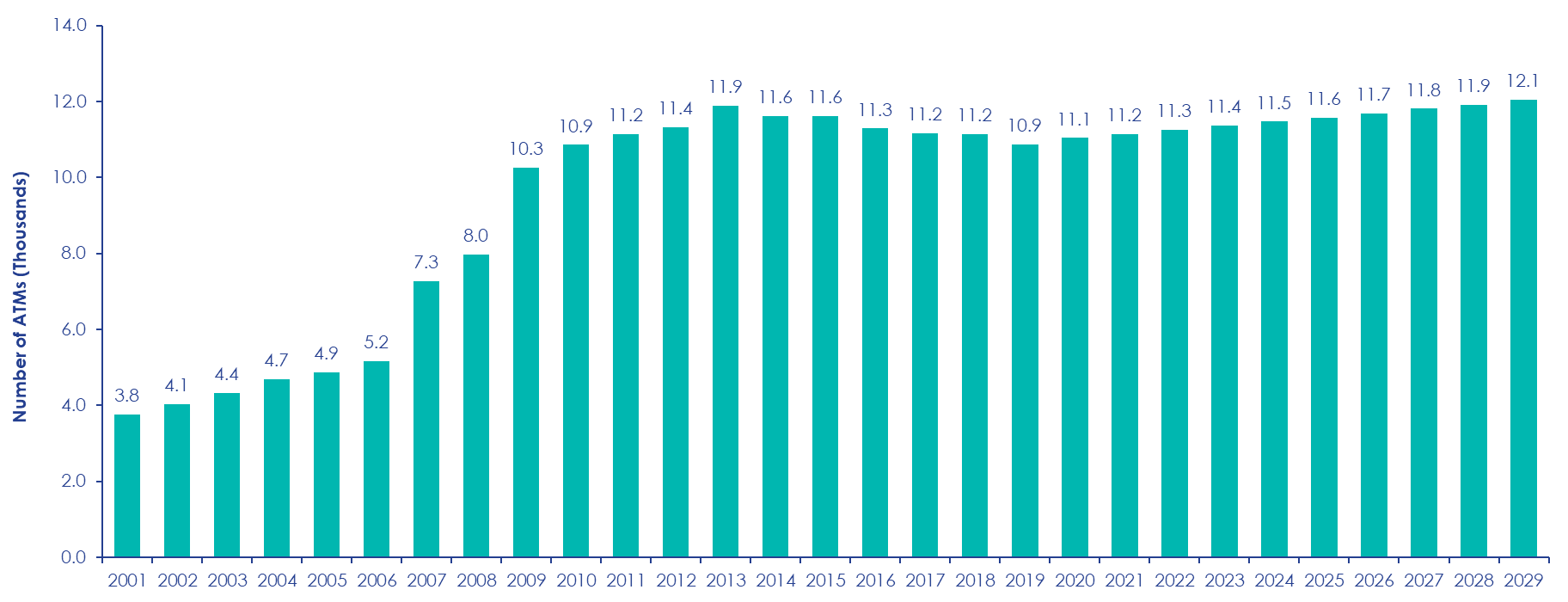
Source: Malaysia: Total Number of ATMs in thousands 2001-2029 | Statista
Why Banks need to focus on their core business and outsource their ATM managed services to third party providers.
One of the key strategies is ATM outsourcing, which offers a compelling solution for banks is to optimize their ATM operations and enhance the value proposition of their networks. By partnering with specialized ATM management providers, banks can leverage expertise, resources, and economies of scale to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve service quality. This approach not only ensures the continued availability and reliability of ATM services but also frees up resources for banks to focus on core business functions and innovation.
Furthermore, ATM outsourcing enables banks to stay agile and responsive to market dynamics, allowing them to adapt quickly to changing consumer preferences and technological advancements. With the support of outsourcing partners, banks can explore new revenue streams, enhance ATM functionalities, and expand their reach into undeserved communities, thereby driving the sustainable growth of their ATM networks.
The key innovations driving success in the ATM industry in Southeast Asia
In Southeast Asia, the ATM industry is undergoing wave of innovation, driven by technological upgradations and evolving consumer choices. These innovations not only enhance the functionality and accessibility of ATMs but also contribute to the overall success and relevance of ATM networks in the region.
- Biometric Authentication Technology
One notable innovation in the ATM industry is the introduction of biometric authentication technology. Biometric ATMs, equipped with fingerprint or facial recognition systems, offer a higher level of security and convenience for users. By eliminating the need for physical cards or PINs, biometric ATMs provide a seamless and frictionless banking experience, particularly in regions where identity theft and fraud are prevalent concerns. - Integration of Contactless Payment Technology
Another innovation reshaping the ATM landscape is the integration of contactless payment technology. ATMs equipped with contactless card readers or near-field communication (NFC) capabilities enable users to conduct transactions swiftly and securely using their mobile phones or contactless cards. - Intelligent ATM Management Systems
The advent of intelligent ATM management systems is revolutionizing the way ATM networks are monitored and maintained. These systems leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics to optimize ATM performance, predict maintenance needs, and detect potential security threats in real-time. By proactively addressing operational issues and ensuring maximum uptime, intelligent ATM management systems enhance the reliability and efficiency of ATM networks, thereby driving their success in Southeast Asia. - CRM Integrated Cash Recycling Technology
The rise of CRM integrated cash recycling technology represents a significant advancement in ATM functionality. These cash recycling ATMs allow user to deposit and withdraw cash simultaneously, thereby reducing the need for cash replenishment and optimizing cash management processes for banks. This innovation not only lowers operational costs but also improves cash availability and uptime, making ATM networks more resilient and cost-effective in serving diverse customer needs.
In conclusion, the future of cash in Southeast Asia is heavily dependent on the evolution of ATM networks. However, ATM outsourcing represents a strategic imperative for banks looking to navigate this transformation successfully as they focus their energies on their core business.
By embracing innovation, collaboration, and forward-thinking strategies, banks can ensure that ATMs remain a cornerstone of the financial ecosystem, driving financial inclusion, empowerment, and resilience in the region for years to come.
(This blog was first published in ATMIA Newsletter - March 2024)
Upgrade to Next-Gen Payments Technology
The rapid evolution of payment technology demands forward-thinking strategies. Our guide offers detailed insights to help you modernize your systems and keep pace with industry advancements. Prepare for the future—download your guide today!
Read More About:
Card Issuing
Switching
ATM Management
Payment Platform
Dynamic Currency Conversion
Payment Hub
Real-Time Payments
Comments

Biswajit Jha
Biswajit Jha is a seasoned professional with over 25 years of experience in the banking and payment industry, focusing on Transaction Channels, Alternate Payment Channels, and Systems across Asia and Europe. Currently serving as the Managing Director at Euronet, EFT Malaysia, he is known for his expertise in driving overall business operations and strategy in the region. Biswajit has a proven track record of being a catalyst for transformational growth in the organizations he has worked with. His skills include building strong and diverse client-centric teams to achieve desired outcomes. Prior to Euronet, he held various leadership roles at Diebold Nixdorf across APAC, Middle East, and Europe. Biswajit has also worked with esteemed organizations such as Standard Chartered Bank, ANZ, TCS, BNP Paribas, and Tata Motors. He holds a Master of Business Administration in Marketing (MBA) from S. P. Jain Institute of Management and Research (SPJIMR), Mumbai, and a Bachelor of Engineering from Motilal Nehru Institute of Technology.


